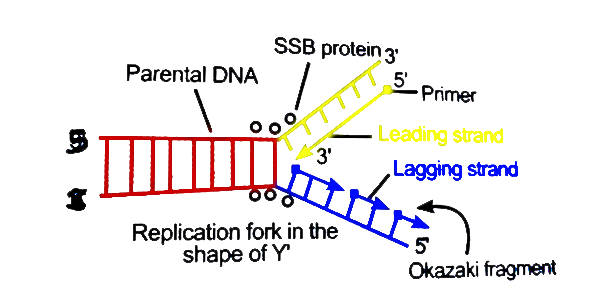
The Mechanism of DNA replication is a complex phenomenon which involve the following
steps:
- Origan of replication site:-
DNA is a long chain of polynucleotides. It has many replication units called
replicons. Replication is iniated at each replicon by producing a nick (cut) in one
of the strands of a specific initiation point called (ori-site). The nick is
produced by an enzyme called Endonuclease
- Activation of deoxyribonucleotides:-
Free nucleotides present in the nuclei plasm as deoxyribonucleotides monophosphates
(DNHPS) -dAMPS, dGMPs dCMPS, and dTMDs are activated into triphosphates (dAMPS,
dGTPTs, dCTPs, dTTPs) with the help of an enzyme phosphorylase in the presence of
ATP. This process is known as phosphorylation.
- Unwinding of DNA helix:-
The unwind of two DNA strands in the presence of an enzyme helicase, which breaks
the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides. Due to the unwinding of two DNA strands,
a y-shaped fork called replication fork is formed. Now both separated DNA strands
are called templates.
- Formation of RNA primes:-
Replication is guided by RNA primer. RNA primer is a small strand of RNA that is
synthesized by an enzyme primase. Primase is attached to the template DNA at a site
called initiation site from where the DNA synthesis begins.
Replication always initiated from 5' direction to 3' direction.
- Elongation of new strand:-
- Once, the primer stand is formed, DNA replication begins with the help of DNA
polymerase III (in prokaryates) and DNA polymerizes (in eukaryote) along with
ATP and MG²⁺
- Nucleotide chain formation proceeds from the initiation side by adding new
bases.
- Replication proceeds on both the template DNA strands. Therefore, the
replication process is bidirectional. Replication is continuous on one template
strand i.e single DNA primer is responsible for the formation of whole strand.
Thus, a new strand is formed which is called a leading Strand
- After a formation of a new nucleotide chain is completed RNA primer is removed
and the gaps get filled with the complementary bases
- Termination:-
The replication is terminated when ever two replication forks meet.
- Proof-reading and DNA repair:-
Sometimes the wrong bases may be inserted during replication. It is an error. The
probability of which error is about once per 100000 nucleotides. The error is
connected is by inserting the correct nucleotides. This process is called
Proofreading.
The replication in which half of the original DNA is conserved and half is the
newly synthesized one is called semi-conservative mode of replication of DNA.